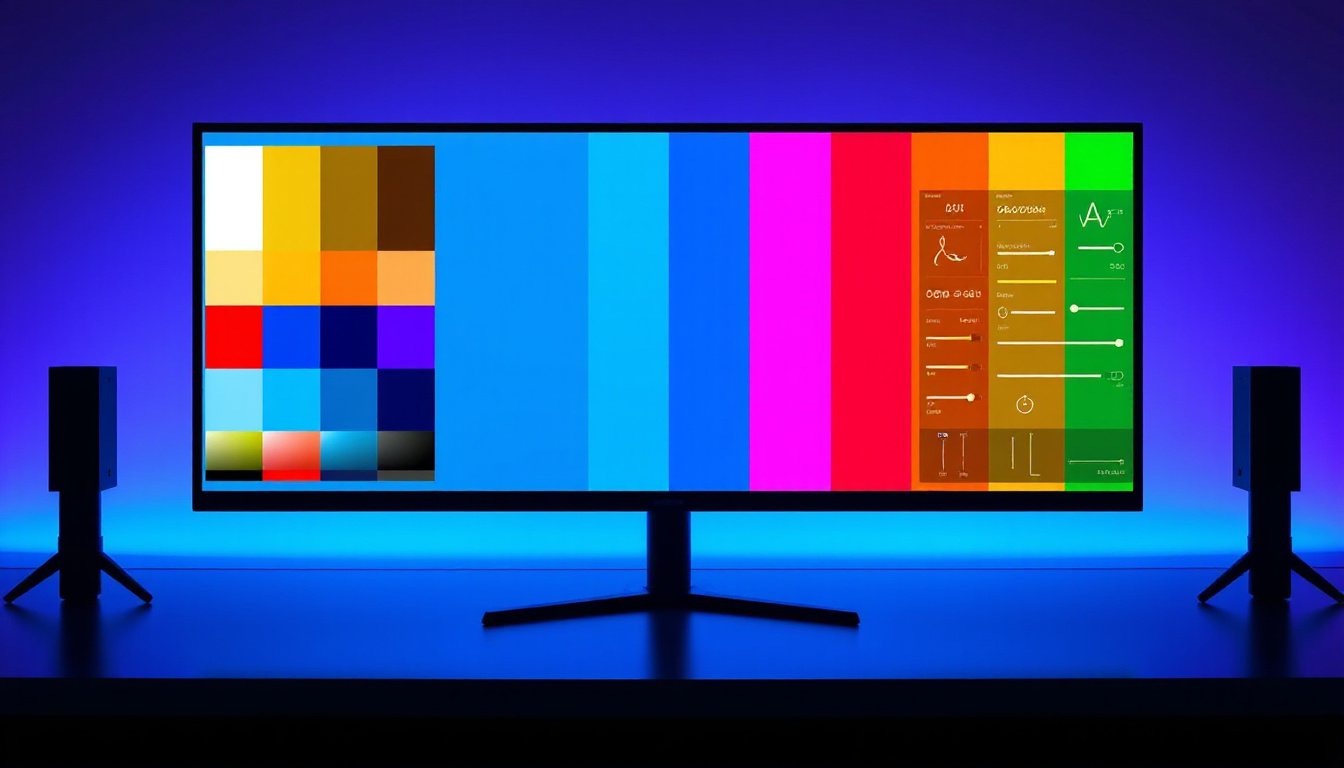
In the realms of digital imaging, from professional photography and medical diagnostics to entertainment and product design, color accuracy stands as a cornerstone of visual fidelity. But what exactly is color accuracy, why does it matter, and how can it be measured and ensured in digital displays and cameras? This comprehensive guide unravels the essentials of color accuracy, the factors influencing it, and methods to achieve the truest representation of colors in your digital experience.
What is Color Accuracy?
Color accuracy refers to how faithfully a device—be it a camera or a display—reproduces colors as compared to their real-world or intended reference colors. Imagine viewing a sunset-themed photo; accurate colors would ensure that the reds, oranges, and purples look just as vivid and natural as when observed firsthand. The goal is to minimize discrepancies between actual colors and their digital representations.
For cameras, color accuracy involves capturing scenes without shifts or distortions in hue, saturation, or brightness. For displays, it means showing colors as intended by content creators or industry standards without unintended tints or washes. Poor color accuracy can mislead viewers or users, diminish immersive experiences, and reduce trust in visual data.
Why Is Color Accuracy Important?
Realistic and Consistent Visuals
Accurate colors are essential to maintaining realism, whether you’re analyzing medical images, inspecting product quality, monitoring surveillance footage, or enjoying cinema. An image with a blue or yellow tint might distract or cause misinterpretations. For example, in healthcare, subtle color differences can impact diagnostic decisions.
Industry Standards and Uniformity
To achieve consistency across devices and media, industries adopt color standards like Rec. 709, established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Rec. 709 specifies the color gamut, resolution, frame rate, and other parameters for HDTV content, ensuring that video on different platforms maintains consistent color presentation.
Emotional and Aesthetic Impact
In entertainment, accurate colors affect mood and storytelling. Films or games with unnatural color tones can disrupt immersion and emotional connection, while precise colors help convey the creator’s vision.
Core Concepts in Color Accuracy
White Balance
White balance (WB) calibrates the baseline white color under varying lighting conditions. Since natural and artificial light sources have different color temperatures—measured in Kelvins (K)—white balance corrects for warm (lower Kelvin, yellow/red hues like incandescent lights) or cool (higher Kelvin, blue/white hues like cloudy daylight) lighting. This correction removes color casts to ensure that whites appear truly white, providing a foundation for all other colors.
Digital cameras and displays use white balance settings to adjust rendering dynamically or through presets. However, automated white balance can struggle in complex lighting, introducing unwanted color casts such as blue, orange, or green tints.
Color Saturation
Saturation describes the intensity or vividness of a color. Higher saturation produces vibrant, rich colors, while lower saturation yields muted, grayscale-like tones. While saturation enhances visual appeal, excessive saturation distorts realism by causing unnatural color bleed or spillover.
Maintaining appropriate saturation levels balances vibrancy with faithful color reproduction, crucial in applications like security surveillance or medical imaging where color integrity supports decision-making.
Color Gamut and Color Space
- Color Gamut: Represents the full range of colors a device can reproduce. A wider gamut covers more hues and shades, enabling richer and more precise color representation.
- Color Space and Profiles: Define how colors are interpreted and displayed. Common color spaces include sRGB (standard for web content) and Adobe RGB (wider gamut for professional imaging). Color profiles ensure consistent color translation across varying devices.

Factors Influencing Color Accuracy
- Sensor Characteristics: In cameras, sensor sensitivity and noise levels affect how colors are captured under different lighting.
- Lens Quality: Optical aberrations from lenses can alter color transmission and introduce distortions.
- Lighting Conditions: The type, temperature, and consistency of illumination significantly affect color capture and display.
- Image Processing Algorithms: Post-capture processing like gamma correction, hue adjustments, and noise reduction can enhance or degrade color accuracy depending on tuning.
- Display Technology: OLED, LCD, LED, and other technologies have distinctive color output capabilities, contrast ratios, and uniformity, influencing accuracy.
- Calibration and Profiling: Regular calibration using industry-standard color charts and instruments aligns device output with expected standards to maintain accuracy over time.
Measuring Color Accuracy: The Delta E Metric
Color accuracy is quantified primarily using the Delta E (ΔE) value, representing the difference between a device’s rendered color and the true reference color.
- Delta E (ΔE): Calculated through models like CIEDE2000 or CIELAB, ΔE considers differences in lightness, chroma, and hue. A ΔE of 0 indicates an exact match, and values less than 1 are typically imperceptible to the human eye. Values up to 2 or 3 may be acceptable depending on the application, but higher values indicate noticeable color inaccuracies.
- Delta C (ΔC): Measures differences in chromaticity (color purity and hue) without considering brightness.
Using specialized colorimeters, spectrophotometers, and calibration software, professionals analyze these metrics to fine-tune devices.
How to Enhance Color Accuracy
For Cameras
- Set accurate white balance matching the ambient lighting.
- Use high-quality lenses to reduce chromatic aberrations.
- Calibrate sensors and optimize image processing pipelines.
- Avoid oversaturating or undersaturating during image processing.
- Perform periodic maintenance and recalibration.
For Displays
- Choose displays supporting wide color gamuts and calibrated color profiles (e.g., Rec. 709, DCI-P3).
- Use professional calibration tools to measure and adjust color output.
- Update firmware to benefit from improved color management algorithms.
- Consider technologies like OLED or high-quality LCDs known for superior color reproduction.
- Account for ambient lighting conditions in the viewing environment.
Conclusion
Color accuracy is a vital aspect of digital imaging that ensures the faithful reproduction of real-world colors in cameras and displays. It affects the authenticity, reliability, and emotional impact of visual content across industries. By understanding key concepts like white balance, saturation, color gamut, and calibration, and by applying precise measurement techniques such as Delta E calculation, users can unlock true colors, bringing their digital imagery to life precisely as intended.
Whether you’re a content creator, healthcare professional, gamer, or casual user, investing attention in color accuracy enhances your visual experiences, ensuring every shade and hue is rendered with authenticity.
By embracing best practices and understanding the science behind color accuracy, your journey into the world of digital color reproduction becomes one of clarity and vivid realism.